ecg lv aneurysm | left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm ecg lv aneurysm Persistent ST elevation after a STEMI can signify a left ventricular (LV) aneurysm. Differentiating LV aneurysm from STEMI is very challenging, as patients with an LV aneurysms are at high risk for cardiac pathology. If . Best overall 2. Best value 3. Best features 4. Best for big families 5. Best for banking 6. Best performance 7. Best for simplicity How to chooseHow we test. The best antivirus software helps.
0 · what is ventricular aneurysm
1 · what is an apical aneurysm
2 · ventricular aneurysm ecg
3 · left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm
4 · left ventricular aneurysm repair surgery
5 · Lv pseudoaneurysm vs true aneurysm
6 · Lv aneurysm vs pseudoaneurysm echo
7 · Lv aneurysm on echo
9490 Bermuda Road, Las Vegas, NV 89123. Applicant Login. Resident Login. Toggle Navigation. Floorplans. Ash Creek; Pine Creek; Oak Creek; Cedar Creek; Willow Creek; Redwood Creek; Specials; . Copper Creek Apartments 9490 Bermuda Road, Las Vegas, NV 89123 (888) 229-1257. Monday to Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:30 PM Saturday: 9:00 .
A left ventricular aneurysm can be diagnosed on ECG when there is persistent ST segment elevation occurring 6 weeks after a known transmural myocardial infarction (usually an anterior MI)..
motoseghe no rolex
A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for . Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the .Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed ST elevations with T wave inversions in the anterolateral leads and up trending troponins. Echocardiogram (TTE) revealed hypokinesia of the anteroapical wall. Emergent cardiac catheterization was .

what is ventricular aneurysm
Persistent ST elevation after a STEMI can signify a left ventricular (LV) aneurysm. Differentiating LV aneurysm from STEMI is very challenging, as patients with an LV aneurysms are at high risk for cardiac pathology. If . Left ventricular aneurysm formation following acute STEMI causes persistent ST elevation on the ECG. ECG Features of Left Ventricular Aneurysm. ST elevation seen > 2 weeks following an acute myocardial infarction. Most commonly seen in the precordial leads. May exhibit concave or convex morphology. Usually associated with well-formed Q- or QS waves
A left ventricular aneurysm can be diagnosed on ECG when there is persistent ST segment elevation occurring 6 weeks after a known transmural myocardial infarction (usually an anterior MI).. A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending artery . Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the diagnosis and management of patients with aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms caused by MI.Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed ST elevations with T wave inversions in the anterolateral leads and up trending troponins. Echocardiogram (TTE) revealed hypokinesia of the anteroapical wall. Emergent cardiac catheterization was significant for distal LAD artery occlusion.
what is an apical aneurysm
ventricular aneurysm ecg
Persistent ST elevation after a STEMI can signify a left ventricular (LV) aneurysm. Differentiating LV aneurysm from STEMI is very challenging, as patients with an LV aneurysms are at high risk for cardiac pathology. If available, the crux of management is comparing the current ECG with an old ECG, which may show the persistent LV aneurysm pattern.

A ventricular aneurysm is a weak spot in a wall in the heart’s lower pumping chambers (ventricles). Heart attacks often cause left ventricular aneurysms. The aneurysm bulges when the ventricle pumps blood, increasing the risk of a life-threatening rupture. Medications or surgery lower the risk of a ruptured ventricular aneurysm.
ECG. 1. 30min - hours. Hyperacute T waves. >6mm limb leads. >10mm precordial leads. Normalizes in days, weeks, or months. 2. Minutes - hours.
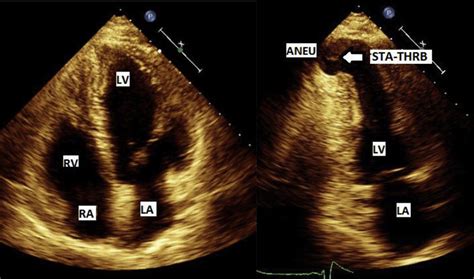
ECG Findings: 1. Normal Sinus Rhythm. 2. Old Anterior Wall Myocardial Infarction. 3. Left Ventricular Aneurysm.The usual ECG findings of left ventricular aneurysm include ST elevation that persists more than two weeks after STEMI, deep Q waves, and the absence of reciprocal ST depressions. Apical four chamber echocardiogram showing severe balloon-like dilation of . Left ventricular aneurysm formation following acute STEMI causes persistent ST elevation on the ECG. ECG Features of Left Ventricular Aneurysm. ST elevation seen > 2 weeks following an acute myocardial infarction. Most commonly seen in the precordial leads. May exhibit concave or convex morphology. Usually associated with well-formed Q- or QS wavesA left ventricular aneurysm can be diagnosed on ECG when there is persistent ST segment elevation occurring 6 weeks after a known transmural myocardial infarction (usually an anterior MI)..
A significant left ventricular (LV) aneurysm is present in 30% to 35% of acute transmural myocardial infarction. The two major risk factors for developing LV aneurysm include total occlusion of the left anterior descending artery . Left ventricular (LV) aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms are two complications of myocardial infarction (MI) that can lead to death or significant morbidity. This topic reviews the diagnosis and management of patients with aneurysms or pseudoaneurysms caused by MI.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed ST elevations with T wave inversions in the anterolateral leads and up trending troponins. Echocardiogram (TTE) revealed hypokinesia of the anteroapical wall. Emergent cardiac catheterization was significant for distal LAD artery occlusion. Persistent ST elevation after a STEMI can signify a left ventricular (LV) aneurysm. Differentiating LV aneurysm from STEMI is very challenging, as patients with an LV aneurysms are at high risk for cardiac pathology. If available, the crux of management is comparing the current ECG with an old ECG, which may show the persistent LV aneurysm pattern.
A ventricular aneurysm is a weak spot in a wall in the heart’s lower pumping chambers (ventricles). Heart attacks often cause left ventricular aneurysms. The aneurysm bulges when the ventricle pumps blood, increasing the risk of a life-threatening rupture. Medications or surgery lower the risk of a ruptured ventricular aneurysm.ECG. 1. 30min - hours. Hyperacute T waves. >6mm limb leads. >10mm precordial leads. Normalizes in days, weeks, or months. 2. Minutes - hours.ECG Findings: 1. Normal Sinus Rhythm. 2. Old Anterior Wall Myocardial Infarction. 3. Left Ventricular Aneurysm.
left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm
left ventricular aneurysm repair surgery
Low Voltage (LV) Switchgears: LV switchgear are designed for systems with a voltage rating of up to 1000V. They are commonly used in residential, commercial, and small industrial applications. LV switchgear typically include circuit breakers, contactors, relays, and fuses.
ecg lv aneurysm|left ventricular pseudoaneurysm vs aneurysm